Choosing the right solar module is often not easy. There are now numerous manufacturers, different sizes, materials and of course prices. Here we answer questions about the possible uses of solar modules and compare different solar modules with each other.
What is solar power needed for?
Before you choose the right solar module, you have already considered what self-generated solar power is needed for. It makes a difference whether you trade solar energy on electricity exchanges or use it to make coffee in a camping tent. Solar modules are used to generate electricity in mountains and in fields, in factories and in houses, on balconies and terraces, in huts, on vehicles, boats and many other places.
Large solar systems with several hundred or even thousands of solar modules are usually operated by companies. Aspects such as the price and the predictability of the earnings are in the foreground.
Smaller solar systems are used for private where handling and convenience play a role in addition to financial aspects. The use is versatile and ranges from feeding into the domestic network to ultra-mobile off-grid power.
Saving electricity consumption from the grid
With grid-connected solar modules, you save electricity from the public grid. The self-generated solar power is fed into the household circuit. This slows down the electricity metre or in some cases even brings it to a standstill. This reduces the amount of electricity drawn from the public power grid.
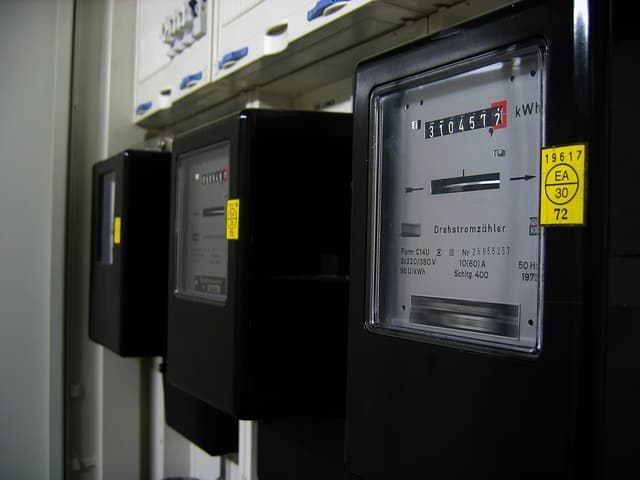

Solar modules generate direct current, which cannot easily be used directly in a household socket. To convert the direct current into conventional alternating current for the socket, grid-connected inverters are used. Inverters are often separate devices, that in some cases are already built directly into the solar module. Inverters are connected to the public power grid via the socket or via electrical distributors. Then they feed electricity into the grid in order to
- supply all consumers upstream of the electricity metre as directly as possible,
- store excess electricity or
- sell or give away the surplus via the public grid.
Solar modules for feeding into the grid often remain in the same place for years or decades and are often firmly connected to the place where they are located.
Off-grid power supply with solar modules
In contrast to the feed-in, there are still many huts, warehouses or houses that are not connected to the public power grid. In the past, diesel generators were often used. Today, solar systems are often the cheaper and more convenient solution here.
Solar power for huts
Depending on demand, a few solar modules are often enough to cover the basic needs of a hut. When choosing the right solar modules for huts, it is important to know whether they should be installed by a professional or by yourself. Especially if only a few solar modules are to be installed, the travel costs of a professional sometimes outweigh the material costs. On the other hand, the solar modules should be installed safely and permanently.
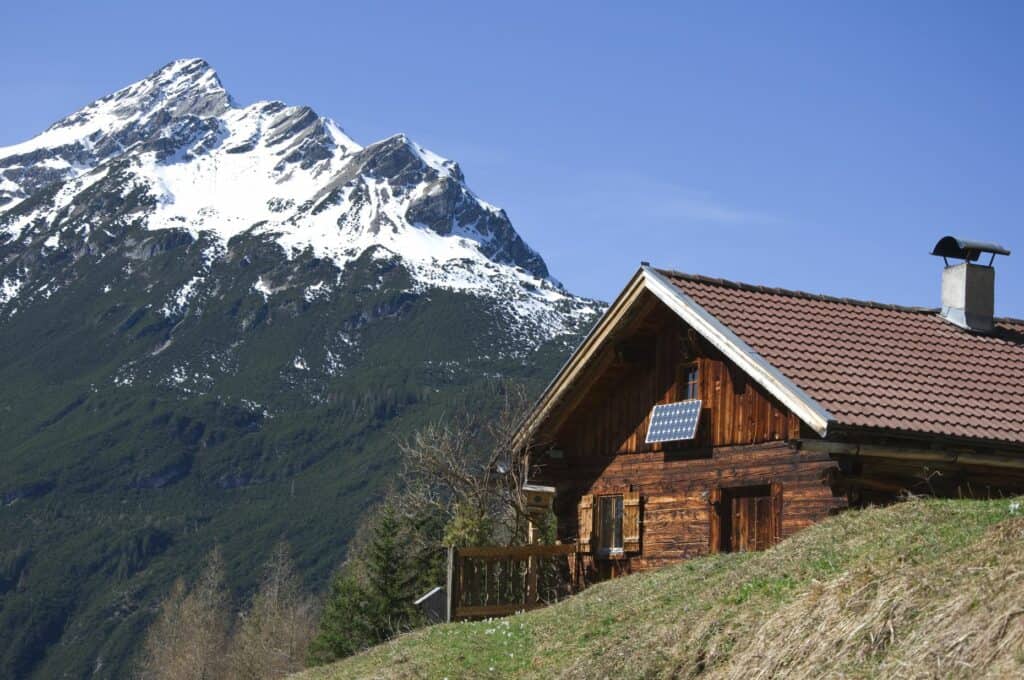

In addition, the huts are often more difficult to reach, which is why the transport route is also taken into account. It may therefore be advantageous to use foldable solar modules or smaller formats.
Mobile power generator at events
Events usually last a few days or weeks. Therefore, the solar modules must not only be easy to set up but also easy to take down again. The materials used must be robust and safe.
Solar modules need light
Solar modules convert light into electricity. Direct sunlight works best for this. Therefore, place the solar module in a location with as much direct sunlight as possible.
Avoid shade
As soon as solar modules are in the shade, the output drops sharply, sometimes to less than 20%. Also avoid partial shading, e.g. at the edge of the solar module. Even small patches of shadow on the solar module can drastically reduce the output. The individual solar cells within the module are connected to form a chain, which is also interrupted by small shadows.
Sometimes there is only indirect, diffuse light or it is a cloudy day. In such cases, the solar modules generate much less electricity than in direct sunlight, but you can still get energy from them even in the shade. In an emergency, the number of solar modules can be increased to achieve the required power.
The sun moves
When choosing the right location, you should also pay attention to how the sun moves throughout the day and year. This also changes the light conditions.

For mobile use, you can simply set up a mobile solar module in a sunnier location. For permanently installed solar modules, you should pay attention to whether you need summer, winter, morning or evening sun.
Increase the power of solar modules
As we already know, solar modules need as much light as possible. Therefore to increase the output, we have the following options:
- Move to a brighter location (e.g. out of the shade into direct sunlight)
- More solar modules to increase the collector area
- More efficient solar modules
How are solar modules mounted?
There are many ways to mount solar modules. Choose the right mounting method depending on where and how long they will be used. Solar modules are screwed, nailed, glued, tied, standing or laid down. They are attached to roofs, walls, railings, poles, vehicles or the ground. Solar modules are used permanently in the same place, mobile or in mixed form.
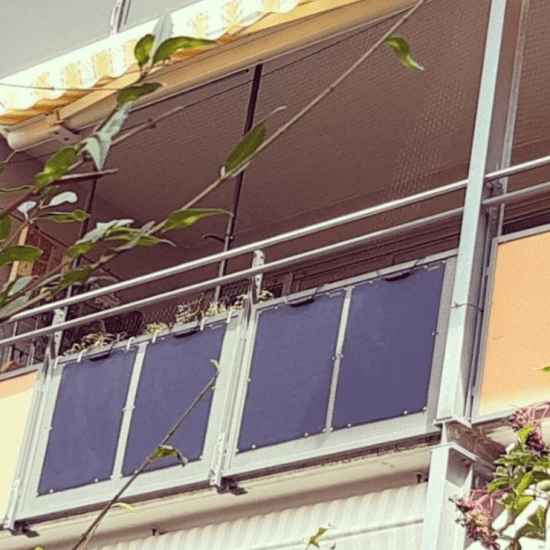
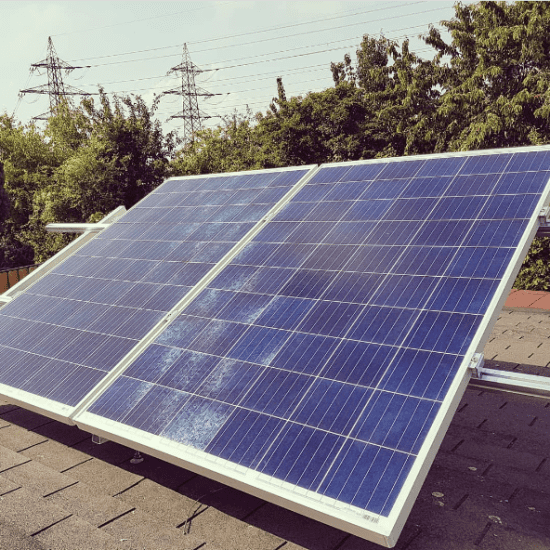
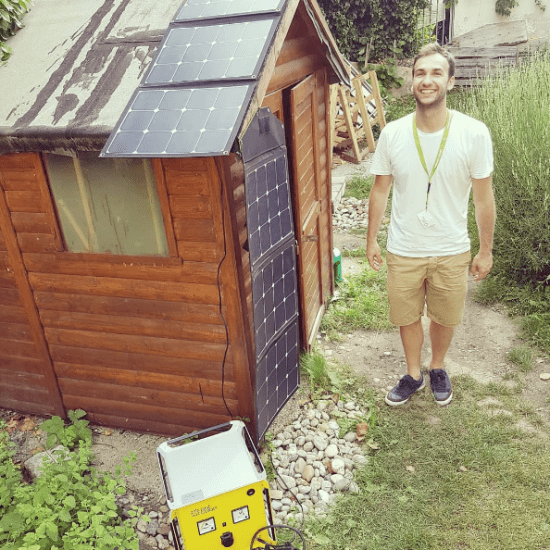

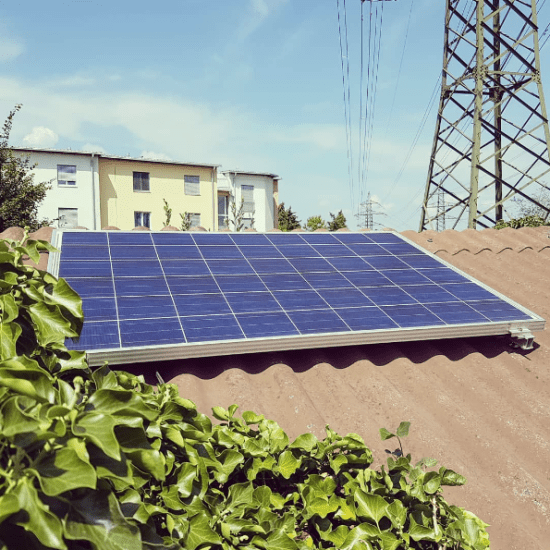
Compare solar modules
If you already have a firm idea about the use of solar energy and a suitable place for solar modules has been found, you can look for a suitable provider.
The majority of solar modules are manufactured in Asia. In terms of safety and quality, they also meet the high European standards. Despite the price pressure, however, some manufacturers have also established themselves in Europe.
Solar panels made of glass last for decades
Solar panels made of glass have been optimised over decades and are produced in large quantities with a high degree of standardisation. The main components are silicon for the glass and solar cells and aluminium for the frame. Both elements are available on earth in almost unlimited quantities.
When properly installed, solar panels made of glass can last for decades. Solar panels made of glass are therefore very popular for power supply on one’s own property. Despite their long life, glass solar panels are inexpensive.
Glass solar panels are surrounded by a metal frame. The connections are located on the back. This requires a mounting construction that permanently fixes the solar panels and at the same time allows access to the connections.
The installation of glass solar panels requires thorough preparation and craftsmanship. Due to the heavy weight of glass panels, several people are usually needed to mount them.
Although solar panels made of glass are very stable and weatherproof, they are not indestructible. If something goes wrong and e.g. a hammer falls on the glass surface, the glass can shatter into many individual parts. Glass solar modules should therefore not be installed in places where vandalism is to be expected.
Glass solar panels
Advantages of glass solar panels
- Long life span
- Weather resistant
- Low price
- Recyclable
Disadvantages of glass solar panels
- Complicated assembly
- High weight
Lightweight plastic solar modules can be easily installed
Solar modules made of plastic weigh up to 70% less than glass modules. This means that these solar modules can usually be handled on their own. Lightweight solar modules also allow them to be used on weak buildings with little residual load-bearing capacity.
Eyelets offer versatile options for fastening, e.g. with nails, screws, cable ties, ropes, wires and much more. Semi-flexible plastic solar modules adapt to slightly curved surfaces.
You must be especially careful when handling them. Solar cells can break if you bend them too much. In particular, larger, semi-flexible solar modules are “wobbly” when handled, which can quickly cause the solar cells to break. The resulting cracks are not visible to the naked eye and reduce performance.
However, the service life is not comparable to that of solar modules made of glass, because plastic discolours, deforms and loses strength over time. If you choose the right manufacturer, plastic solar modules will last for many years.
Plastic solar modules
Advantages of plastic solar modules
- Easy assembly
- Low weight
- For uneven ground
Disadvantages of plastic solar modules
- Not dimensionally stable
- Cell breakage due to incorrect handling
Foldable solar modules for on the move
Mobile use at events, camping and glamping requires solar modules that are both powerful and easy to transport. Two characteristics that foldable solar modules combine.
Foldable solar modules made of plastic weigh significantly less than solar modules made of glass. Plastic also reduces the risk of injury that exists with glass modules due to sharp edges or the risk of breaking.
Foldable solar modules are incorporated into textiles. This makes them very comfortable to handle and offers some extras such as sewn-on feet and pockets for transporting accessories such as plugs and cables.
The textiles incorporated into the solar module discolour due to weathering and sometimes also lose their strength, which is why they age more quickly than other solar modules when used continuously over several months.
Foldable solar panels
Advantages of foldable solar panels
- Quick assembly and disassembly
- Easy transport
Disadvantages of foldable solar panels
- Ageing of the textiles
- Not suitable for permanent installation
Laying cables for solar modules
As a rule, solar modules and electronics are physically separated from each other. To find the right place for solar modules, consider where the self-generated electricity will be consumed and how the power lines will be laid. Power lines are often laid from the outside to the inside. In this case, holes and bushings may be necessary. In the case of bushings, it is often helpful if the plugs are placed on the solar lines after they have been laid.
Also, estimate the required cable length. With solar modules, you will usually find plus (+) and minus (-) separated and therefore lay either one thick cable with two conductors or two separate cables.
MC4 connector on the solar panel

Despite the large number of solar modules, MC4 connectors are very widespread, especially from a module output of about 80 -100 watts upwards. For smaller module outputs, you will find many different connectors or have to make your own connections on the solar module.
MC4 connectors are designed for long-term and fixed outdoor use. Therefore, they can normally only be mounted once on a solar cable. If something is done wrong with the connector, the connector must be cut off and a new connector used. This is annoying if, for example, you have mixed up the plus (+) and minus (-) or have not left enough reserve when laying the cables.
Since they are intended for long-term use, MC4 connectors are difficult to open after they have been plugged together. Some solar modules are supplied with connectors that can only be opened with tools.
You must be careful with MC4 connectors. If they are connected incorrectly, the extra-low voltage can be exceeded.
Observe the precautions when handling electricity
Electricity is harmless up to the so-called extra-low voltage. Individual solar modules can therefore be installed, cables laid and connections inserted by anyone without hesitation. If several solar modules are connected in series, the extra-low voltage can be exceeded and there is a risk of electric shock. Therefore, make sure that no current can flow through the cables during installation or, if necessary, use ready-made cables with pre-assembled plugs.